We are working on improving our portfolio. Case studies about our experience.
Our services
iSenseBot is IoT based solution to capture realtime data in warehouse Continue reading ...
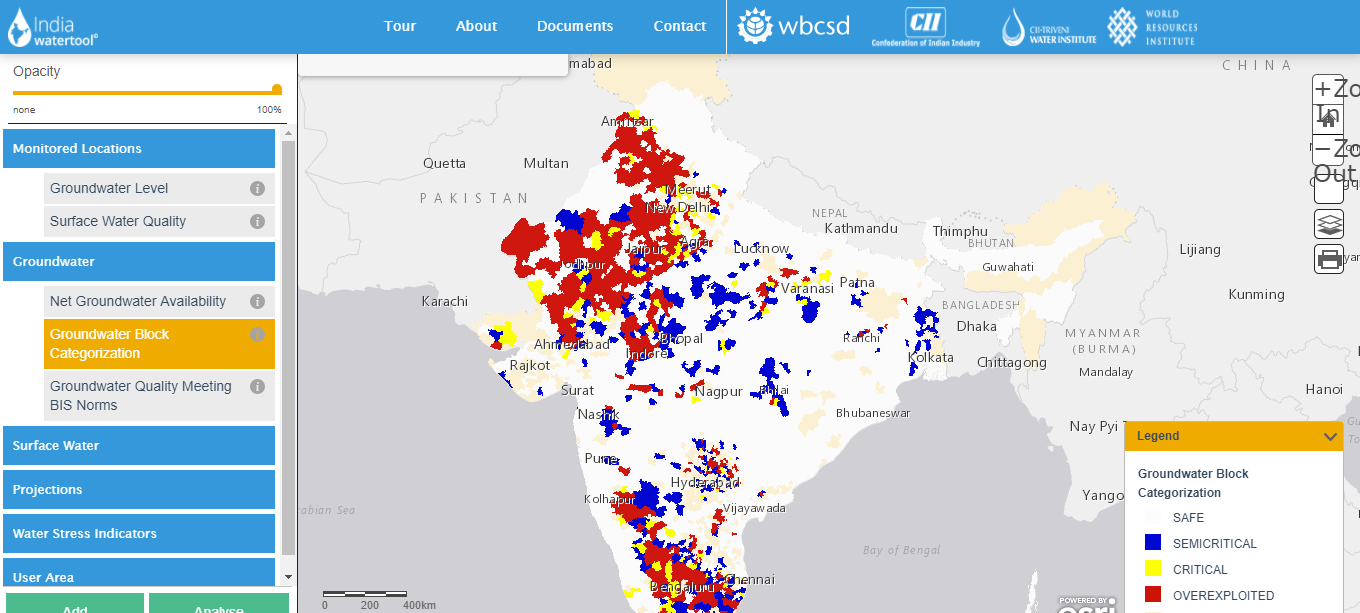
Hydromet Application provides secure real-time data access of automated weather stations.This includes the backend infrastructure to receive, ingest, decode, process, display, and store measurement data from nearly any remote automated weather station. Hydromet Appliccation provides a secure web-page for users to view their data graphically, on a map or in tabular and report forms. Conversely, if you prefer to do your own processing, Hydromet Application delivers raw data (as it is transmitted by the station) using a dedicated, secure download page, updated immediately as your data arrives.
Features/Benefits :
Anytime access to current and historic measurement data collected from remote hydrometeorological monitoring stations.
- Secure password protected log-in for multiple users
- User-established management / administration
- Measurement data backed-up in the cloud and stored for at least one year
- Quickly plot predefined range (ex: 24 hrs, 2-day, 7-day, month, etc or customized date range)
- Compare current or recent measurements from multiple sensors or stations Continue reading ...
The emergence of spatial data infrastructures (SDIs) is closely associated with the efforts of collecting and producing geospatial data, as well as the advancement of surveying and computer technologies. In the past decades, a large amount of geospatial data, such as remote sensing images and GPS locations, have been collected by government agencies such as the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Meanwhile, the fast development of geographic information systems facilitates the derivation of various data products from the collected data, such as topographic maps, land cover data, transportation networks, and hydrographic features. As location‐based services are becoming increasingly popular, vast amounts of volunteered geographic information (VGI) (Goodchild 2007) has also been contributed by the general public through smart mobile devices and social media platforms. In addition, the componentization of GIS brings geospatial services that provide data processing and spatial analysis functions in the general Web environment. The large number of geospatial data, services, maps, and others, however, do not ease the use of these geospatial resources. On one hand, it is challenging to find and access these digital resources which are widely distributed at different government agencies and websites (Li, Wang and Bhatia 2016). Continue reading ...
VR Application provides one area of focus is in creating VR applications that provide realistic visualizations of traffic data, where its utility for traffic management is noted. The integration of real-time data and VR allows traffic management to more easily look at varied layers of transport, while also gaining ability to forecast patterns based on historical or expected patterns. Applications such as APCRDA have incorporated 3D building model data, residents information, real-time and historical traffic data into their platform, allowing for a powerful understanding of city data where everything from current traffic patterns to up-to-date residential information, where the data are applied within a human-computer interaction framework.
Applications with complex data demand have become a major challenge for VRGIS, particularly as these applications have incorporated spatial query functions so that desired multi-dimension information can be found more easily, allowing users to better take advantage of analytical capabilities within GIS while still using VR visualization. Addressing this challenge has included applying multi-task parallel scheduling algorithms that can more quickly process complex data and not just simply look at high volume data. Such approaches allow faster processing of data, allowing for visual and query information to appear more quickly even in more typical desktop environments. Continue reading ...
Augment Reality Provides if you own a smartphone, such as an iPhone or Android, you probably have an app that uses augmented reality (AR). This technology superimposes digital information on whatever you're looking at through your phone's camera. These types of AR apps usually combine an assortment of miniaturized technology devices—optical sensors, accelerometers, GPS, gyroscopes, solid state compasses—along with context-sensitive information, that is delivered as a web service. The service content may be displayed as location-based labels (or billboards) that hover over or in front of objects you see through the camera display. The labels usually present additional information, including photos, but often provide reviews and contact information for things like restaurants, Wi-Fi hot spots, or houses for sale. You might use AR apps to discover and learn more about objects around you. Some AR apps allow you to use your phone camera to perform sophisticated measurements of distances and angles or even track cosmological events such as the azimuth of the sun. Still other AR apps amazingly recognize patterns in photos, diagrams, and bar codes that then link you to additional content or services, such as product reviews, price comparisons, or videos. Continue reading ...
The smart city concept is developing very quickly around the world, because it provides a comprehensive digital environment that improves the efficiency and security of urban systems and reinforces the involvement of citizens in urban development. This concept is based on the use of geospatial data concerning the urban built environment, the natural environment and urban services. The successful implementation of a smart city project requires the development of a digital system that can manage and visualise the geospatial data in a user-friendly environment. The geographic information system (GIS) offers advanced and user-friendly capabilities for smart city projects. The smart city concept aims at developing a comprehensive system that uses geospatial data to enhance the understanding of complex urban systems and to improve the efficiency and security of these systems. This geospatial data concerns the following.
Urban Environment: The urban built environment such as infrastructure, buildings and public spaces.
Natural Environment: The natural environment such as biodiversity, green spaces, air quality, soil and water.
Urban Services: Urban services such as transport, municipal waste, water, energy, health and education. Continue reading ...
A surveying drone offers an enormous potential for business to extract information and monitor the asset. With a drone, it is possible to carry out topographic surveys of the same quality as the highly accurate measurements collected by traditional topographic surveys, but in a fraction of the time. This substantially reduces the cost of a survey and the workload of specialists in the field. Following are benefits of drone based survey.
Cheap and Faster Survey: Capturing geospatial data with a drone is up to five times faster than with the manual land-based methods and requires less human resource.
Accuracy: Drone survey produces thousands of measurements, which can be represented in different formats (orthomosaic, point cloud, DTM, DSM, contour lines, etc). Drone pictures can provide 3D model of the location.
Inaccessible Areas: A drone can fly almost anywhere. You are no longer limited by unreachable areas, unsafe steep slopes or harsh terrain unsuitable for traditional measuring tools. You do not need to close down highways or train tracks, but you can capture data during operation without an organizational overhead. Continue reading ...
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a process that begins with the creation of an intelligent 3D model and enables document management,coordination and simulation during the entire lifecycle of a project (plan, design, build, operation and maintenance).
BIM is used to design and document building and infrastructure designs. Every detail of a building is modeled in BIM. The model can be used for analysis to explore design options and to create visualizations that help stakeholders understand what the building will look like before it’s built. The model is then used to generate the design documentation for construction.
In recent years, there has been a growing necessity for 3D geoinformation in urban planning and infrastructure management to provide a more realistic representation of urban areas and the built environment. A key concept in public infrastructure management is Life Cycle Asset Management (LCAM), which aims to improve the decision making in each phase of the life cycle of infrastructure assets, such as road and utility networks, civil structures, and green areas. Traditional systems in LCAM are limited in terms of analysis and visualization opportunities due to the use of simpler tools like tables. In this respect, Geographic Information System (GIS) solutions have been widely integrated in LCAM to optimise the administration and monitoring of infrastructure assets. Continue reading ...
An inventory management system is a tool that allows you to track goods across your business’s supply chain. It optimizes the entire spectrum spanning from order placement with your vendor to order delivery to your customer, mapping the complete journey of a product.
Features of our Inventory Order Management System
- Dashboard Chart & Graph
- Branch
- Warehouse
- Product
- Vendor
- Purchase Order
- Receiving
- Customer
- Sales Order
- Shipment
- Transfer Order
- Goods Receive
- Goods Issue Continue reading ...
Supply-chain-management software (SCMS) is the software tools or modules used in executing supply chain transactions, managing supplier relationships and controlling associated business processes.
Features of our Supply Chain Management System
- Dashboard Chart & Graph
- Barcode
- Excel Like Grid Filter
- 6 Modules With 25+ CRUD Forms
- Customer Type
- Customer
- Sales Type
- Sales Order
- Shipment Type
- Shipment
- Invoice Type
- Invoice
- Payment Receive
- Vendor Type
- Vendor
- Purchase Type
- Purchase Order Continue reading ...
Machine learning has been a core component of spatial analysis in GIS. These tools and algorithms have been applied to geoprocessing tools to solve problems in three broad categories. Classication: Classification allows you can use support vector machine algorithms to create land cover classification layers. Clustering: Clustering lets you process large quantities of input point data, identify the meaningful clusters within them, and separate them from the sparse noise. Prediction: Prediction algorithms such as geographically weighted regression allows you to use geography to calibrate the factors that help you predict. These methods work well in several areas and their results are interpretable, but they need experts to identify or feed in those factors (or features) that affect the outcome that we’re trying to predict.
One area of AI where deep learning has done exceedingly well is computer vision, or the ability for computers to see. This is particularly useful for GIS, as satellite, aerial and drone imagery is being produced at a rate that makes it impossible to analyse and derive insight from through traditional means.
The simplest is Image Classification, in which the computer assigns a label, such as ‘cat’ or ‘dog’ to an image. This can be used in GIS to categorize geotagged photos. Continue reading ...
We are experting in developing following GIS Applications in both the opensource and ESRI platform.
Web GIS: We can build Web GIS Solution with following features.
- Supports Google map, Bing map, Yahoo maps and Open Street Map as base layer.
- All common GIS functionality like PAN, Zoom In, Zoom Out, Info Tool is available in the application.
- Supports Google map, Bing map, Yahoo maps and Open Street Map as base layer.
- All common GIS functionality like PAN, Zoom In, Zoom Out, Info Tool is available in the application.
- Supports data download in the form of Image, MS Excel, CSV, PDF and MS Word.
- Supports Google map, Bing map, Yahoo maps and Open Street Map as base layer.
- All common GIS functionality like PAN, Zoom In, Zoom Out, Info Tool is available in the application.
- Data can be queried by attribute and geometry. Continue reading ...
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Services
Our Processes
Industries We Work With
Insurance
Government and Fuding Agency
Climate Change
Agriculture and Forestry
Water Resources
Disaster Risk Reduction
Land and Infrastructure
Hydromet
Smart Cities
Utilities