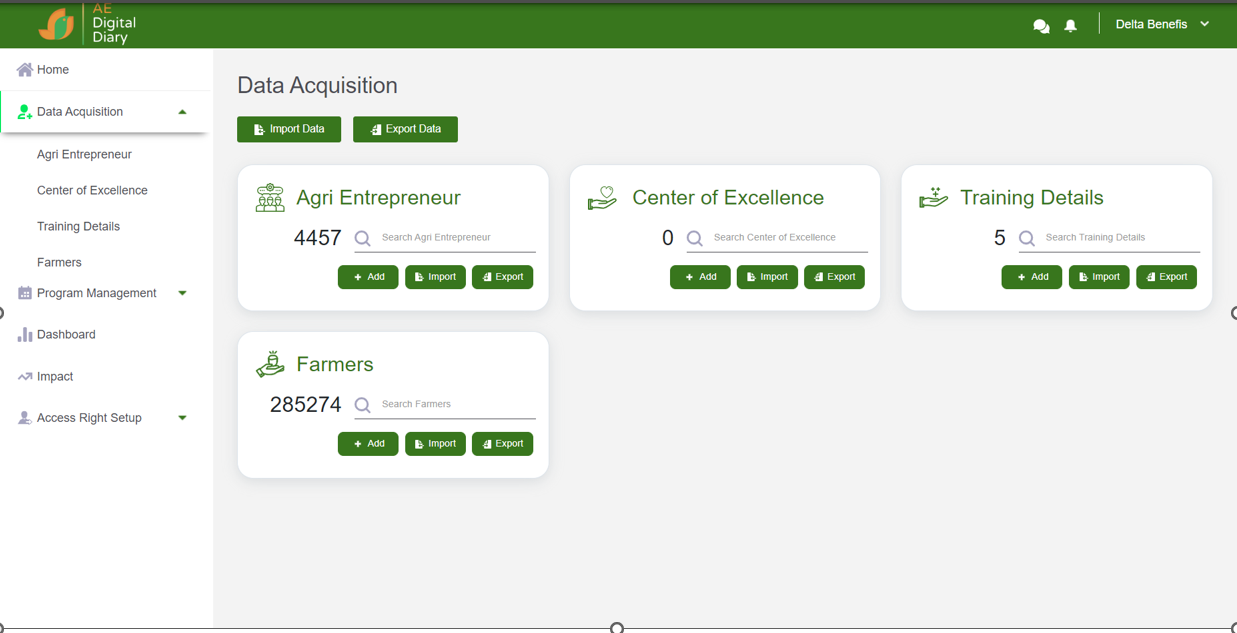
Agriculture/Livestock And Forestry
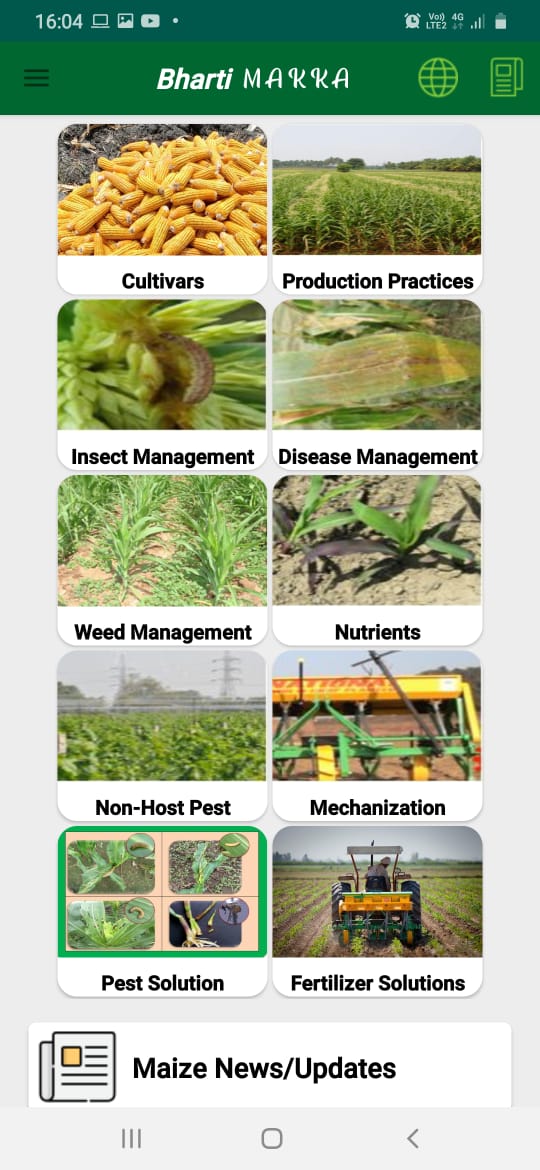


Bharati Makka App Project
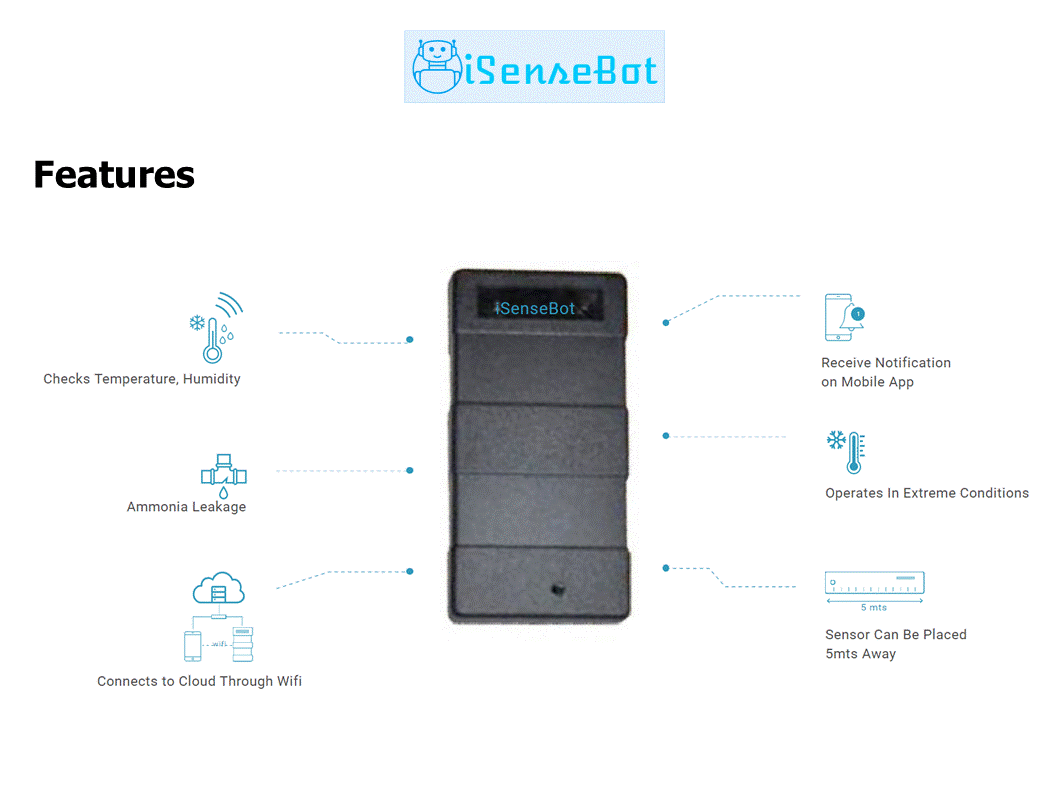
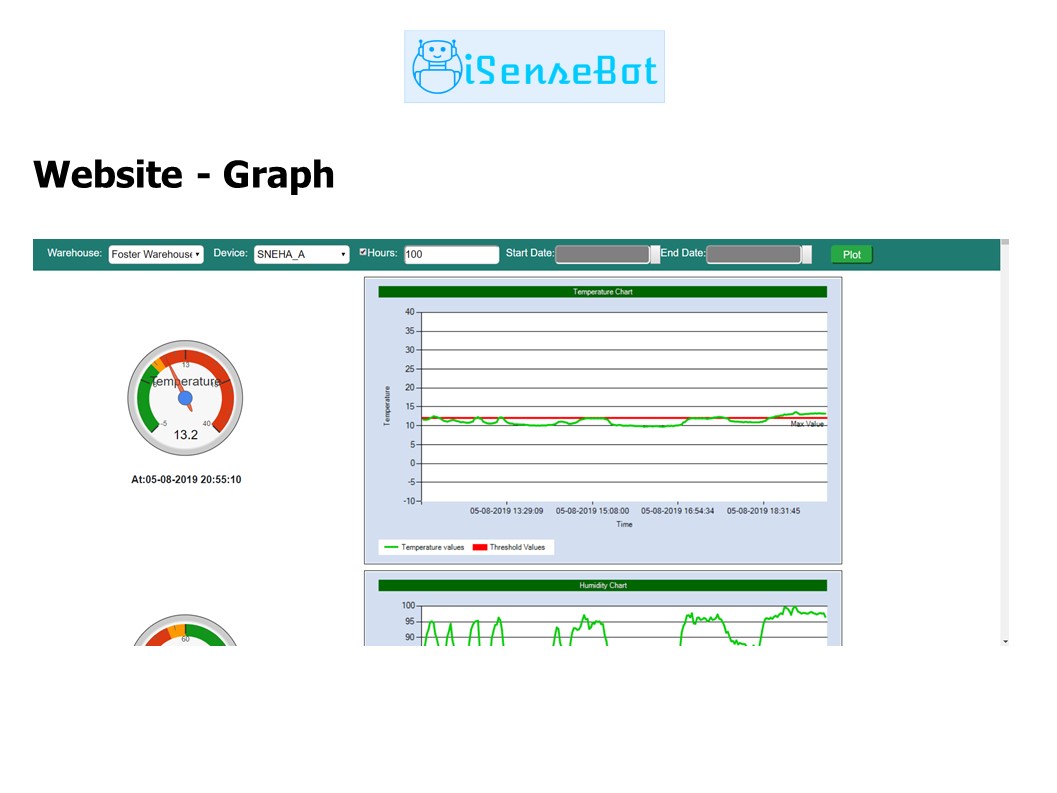
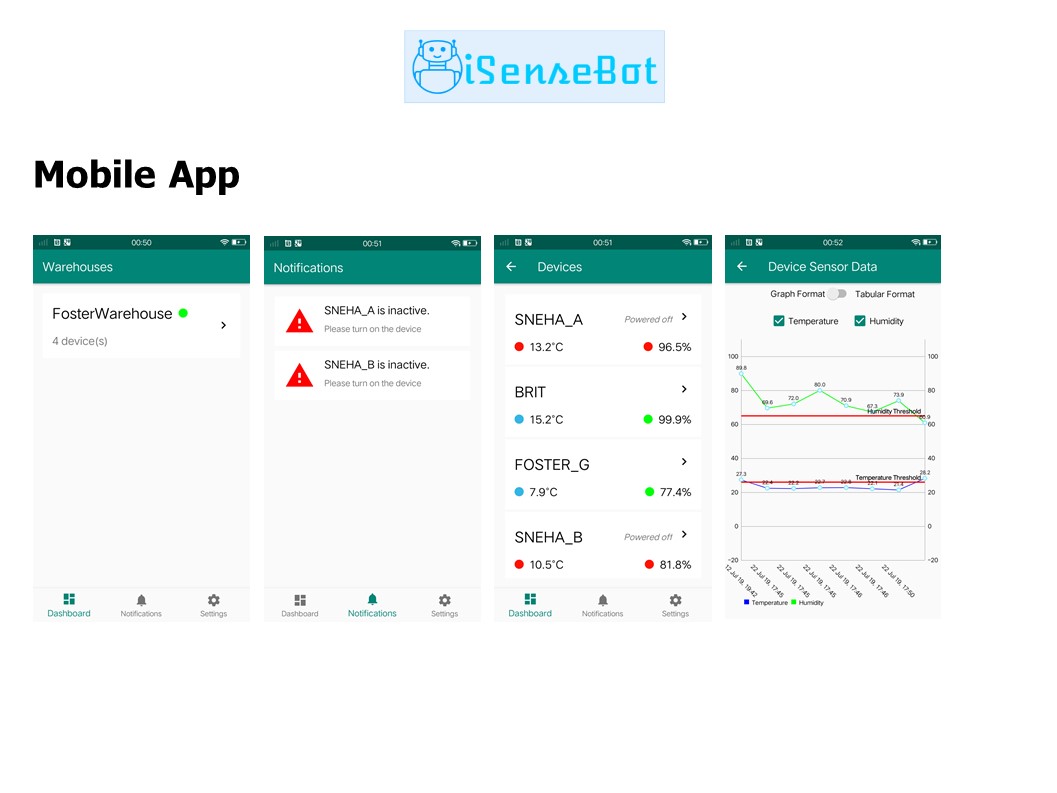
iSenseBot Project

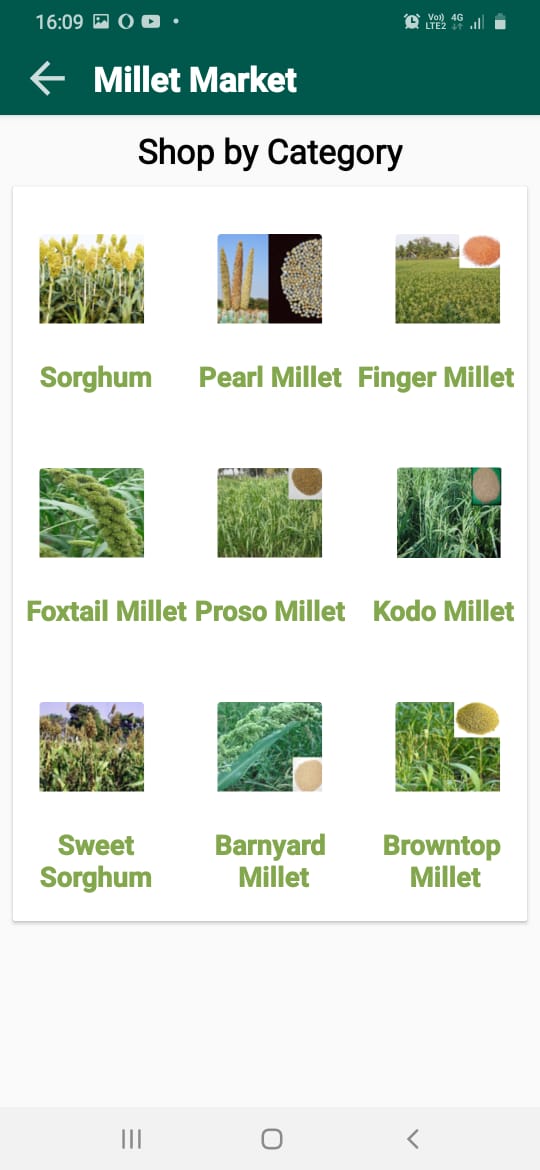
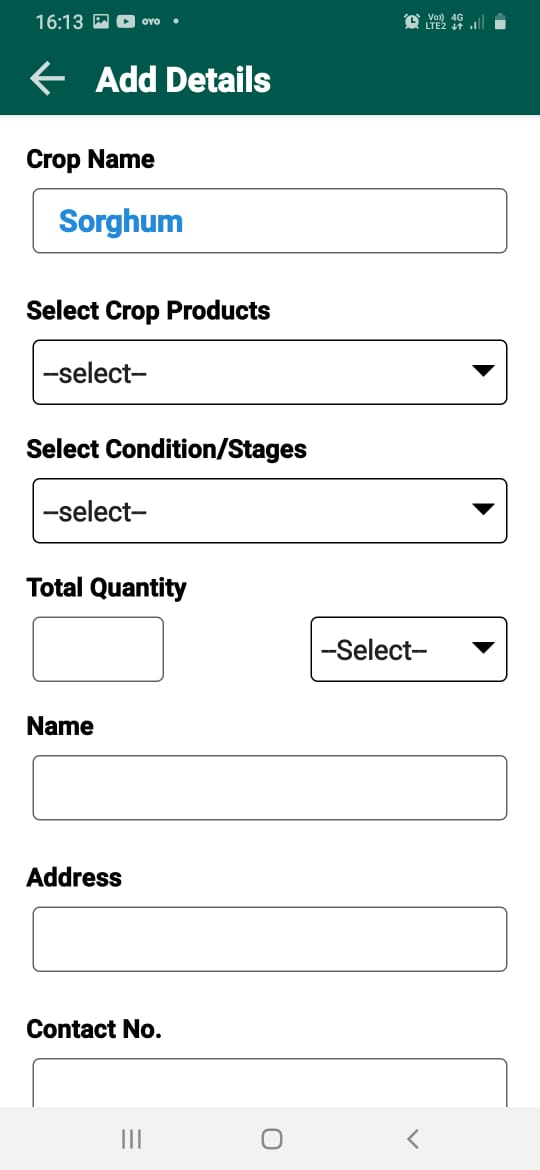
Millet Market Project
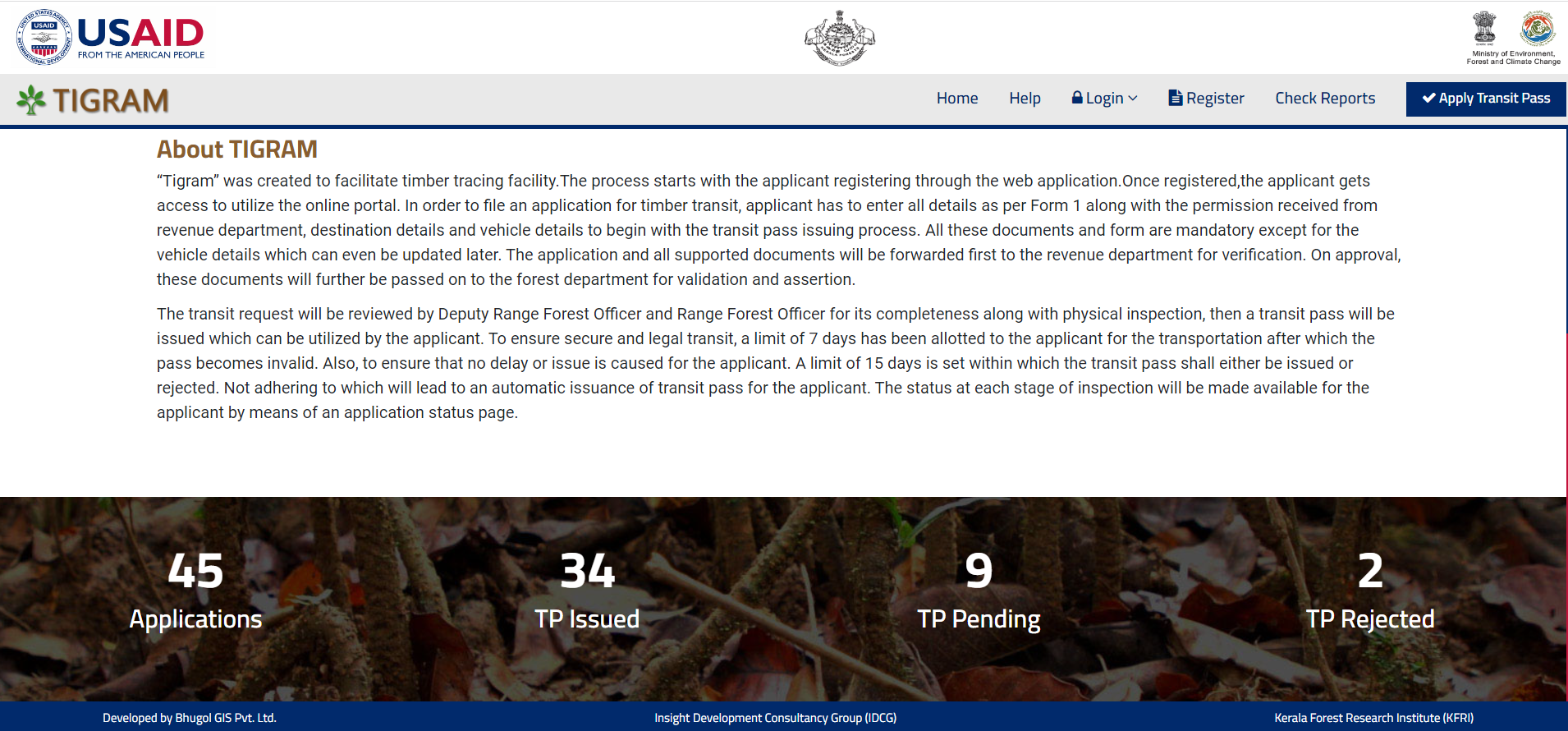
TIGRAM Project
Van IT Project

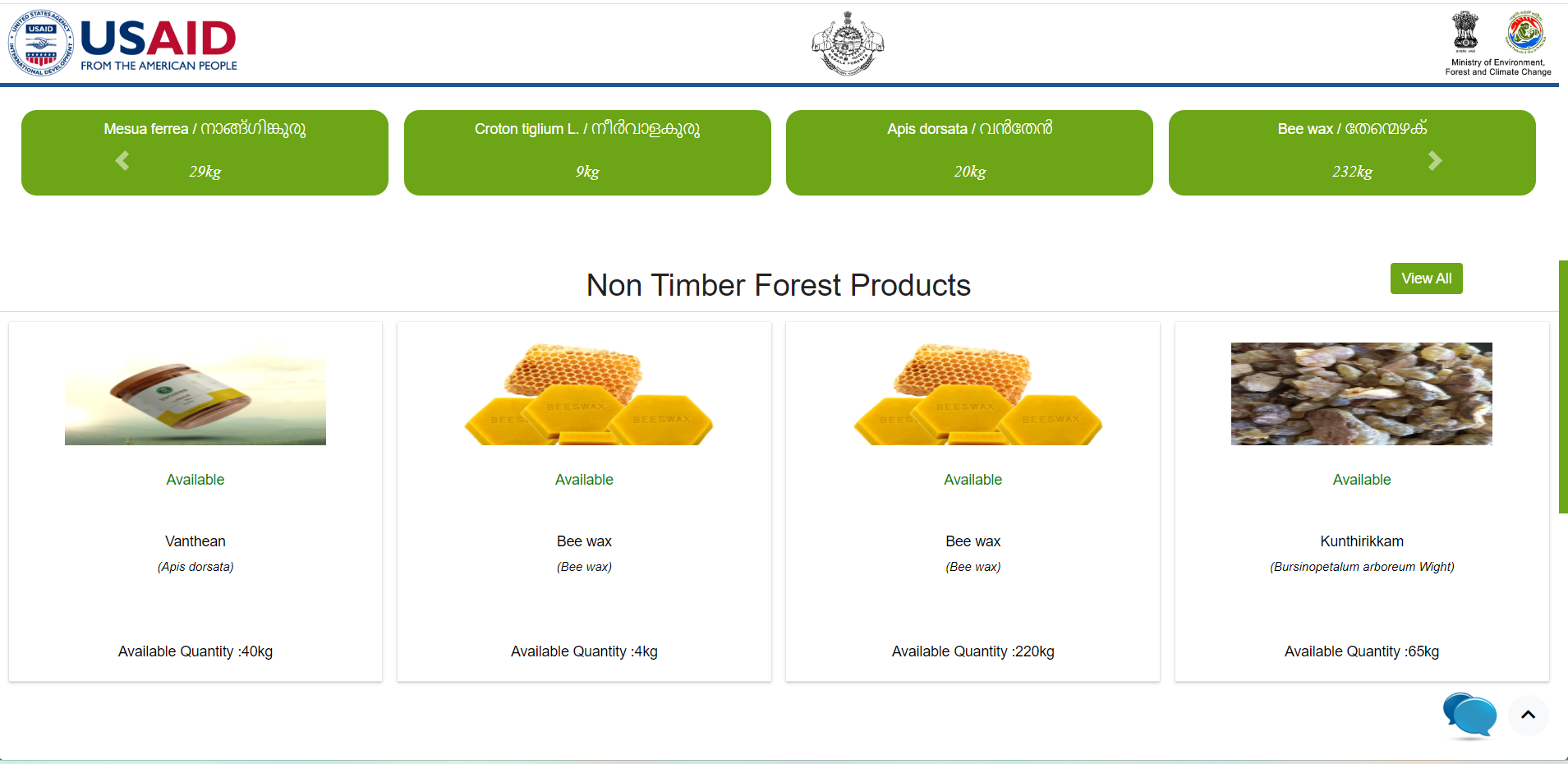
NTFP Project

Child Fund Project

livestock Project

AEGF (Agri Entrepreneurship Growth Fund)