Government and Funding Agency
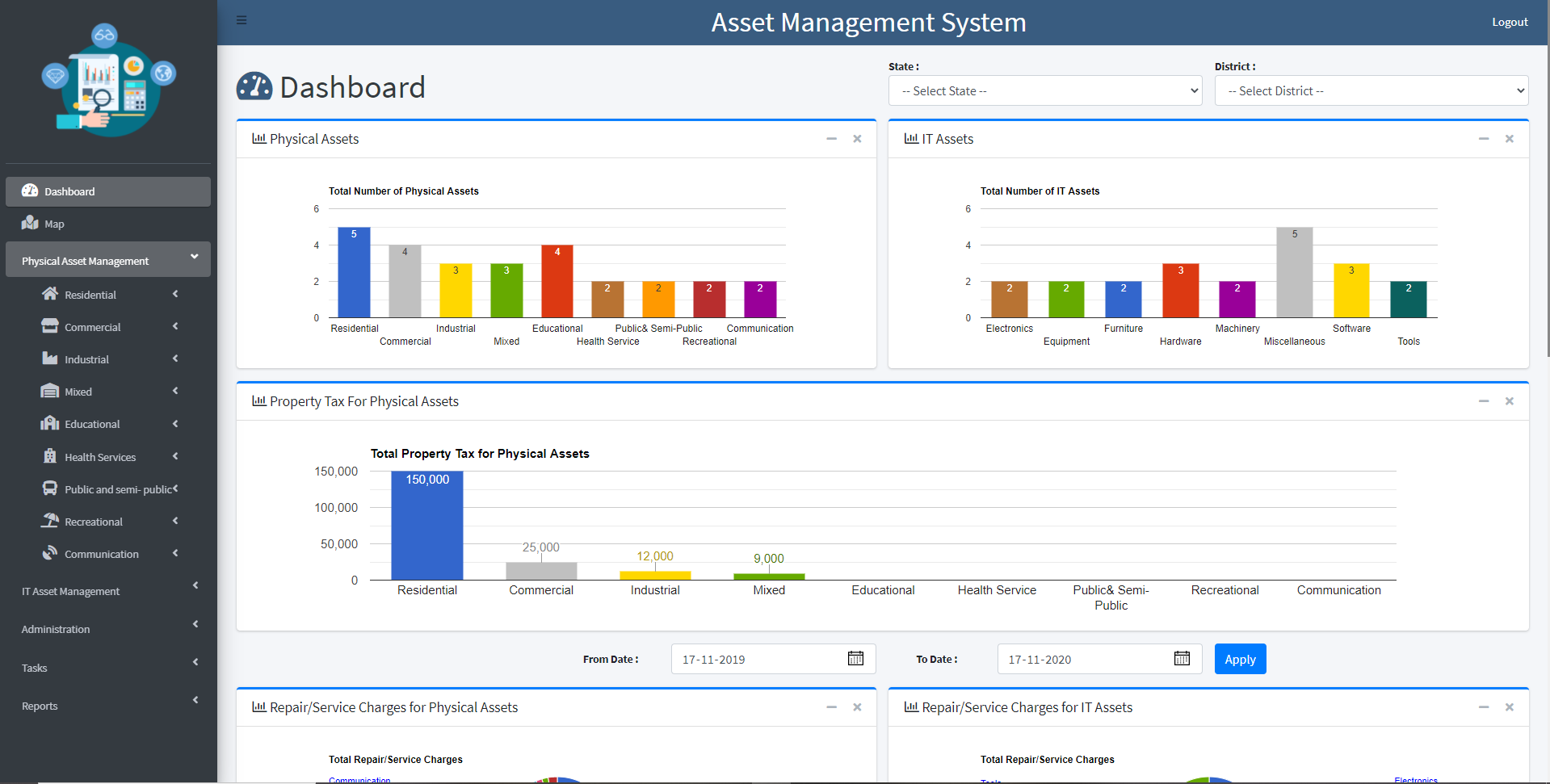
AMS Project

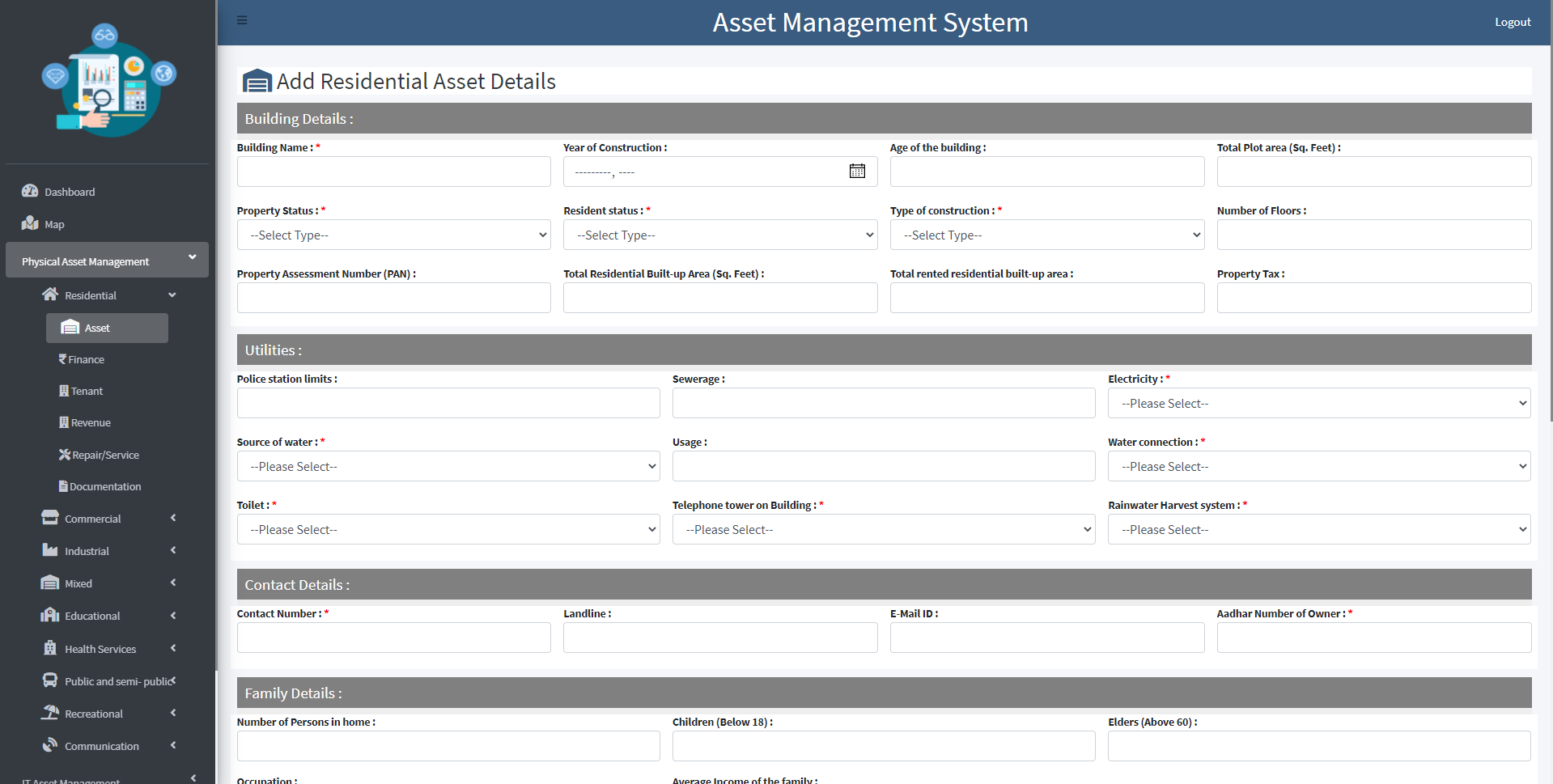
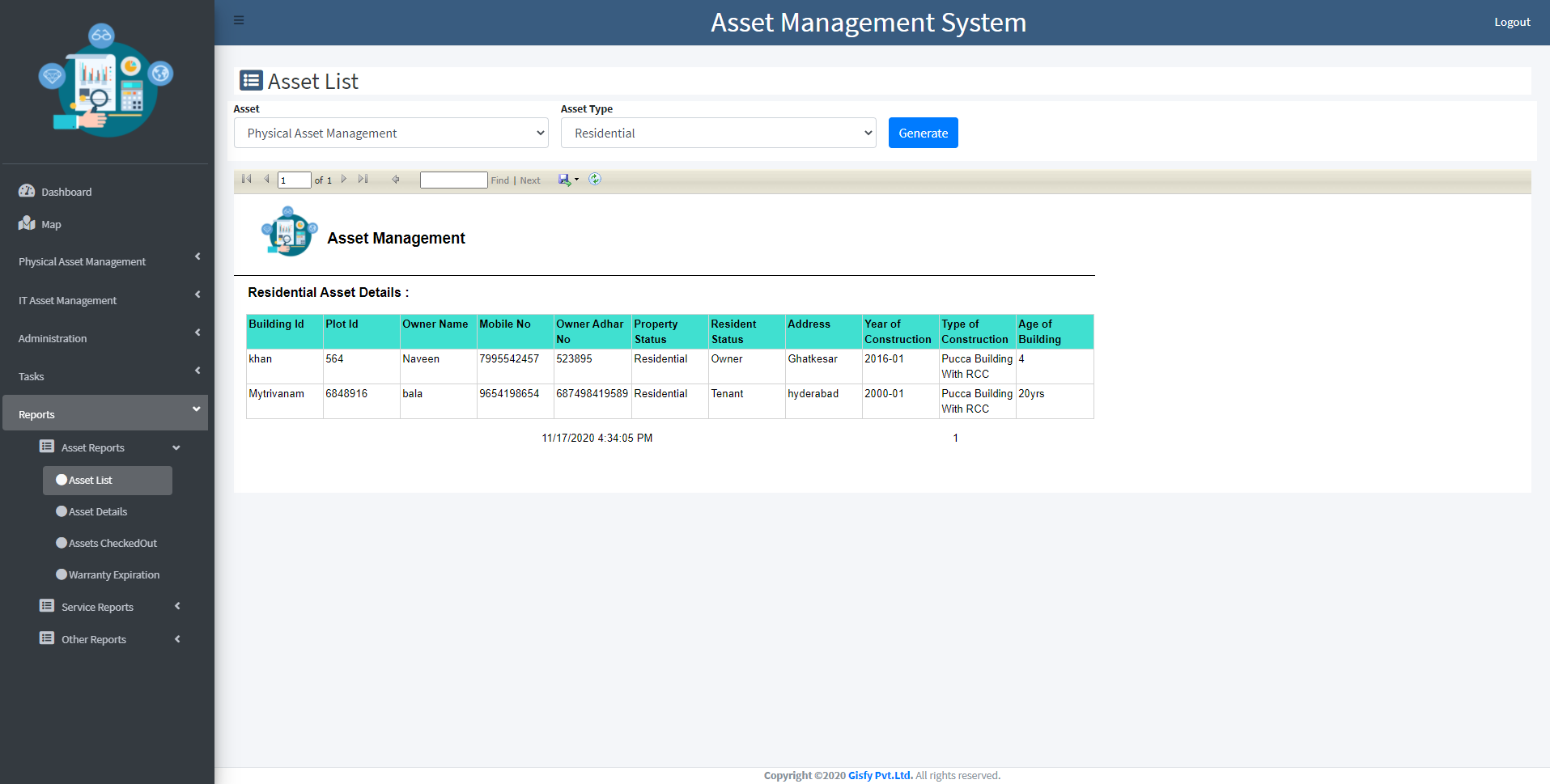
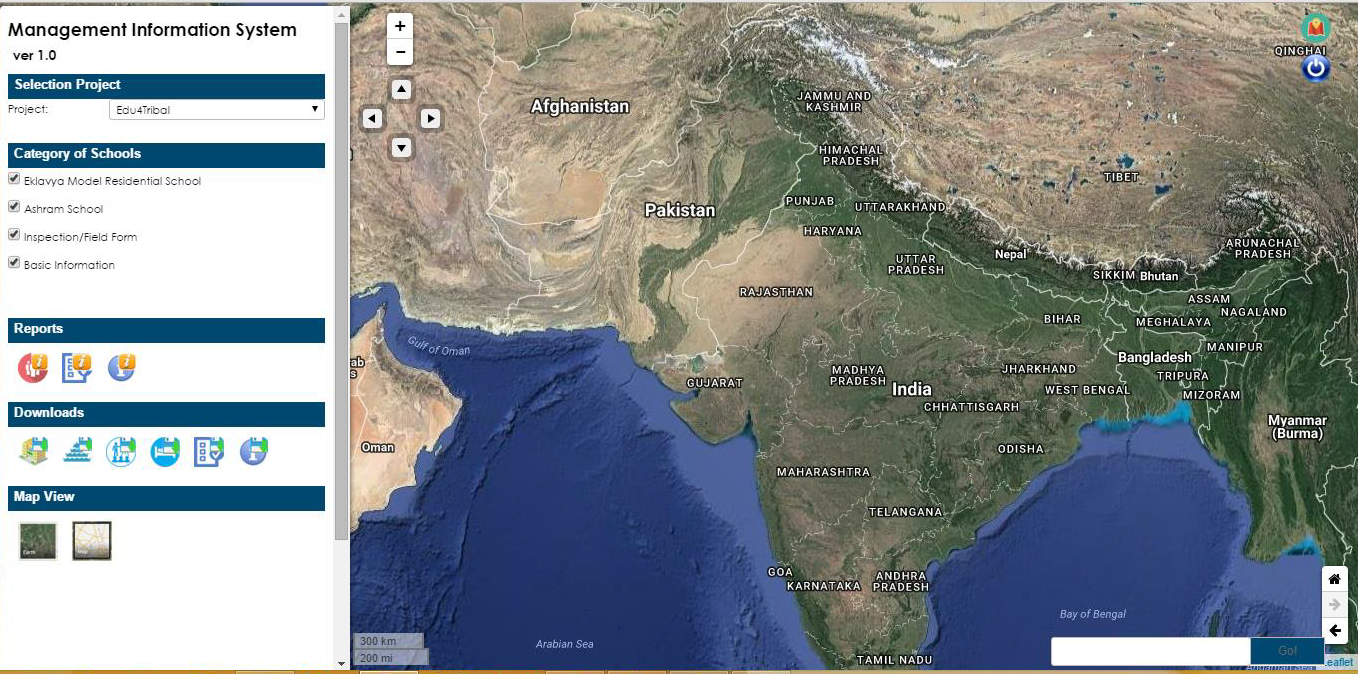
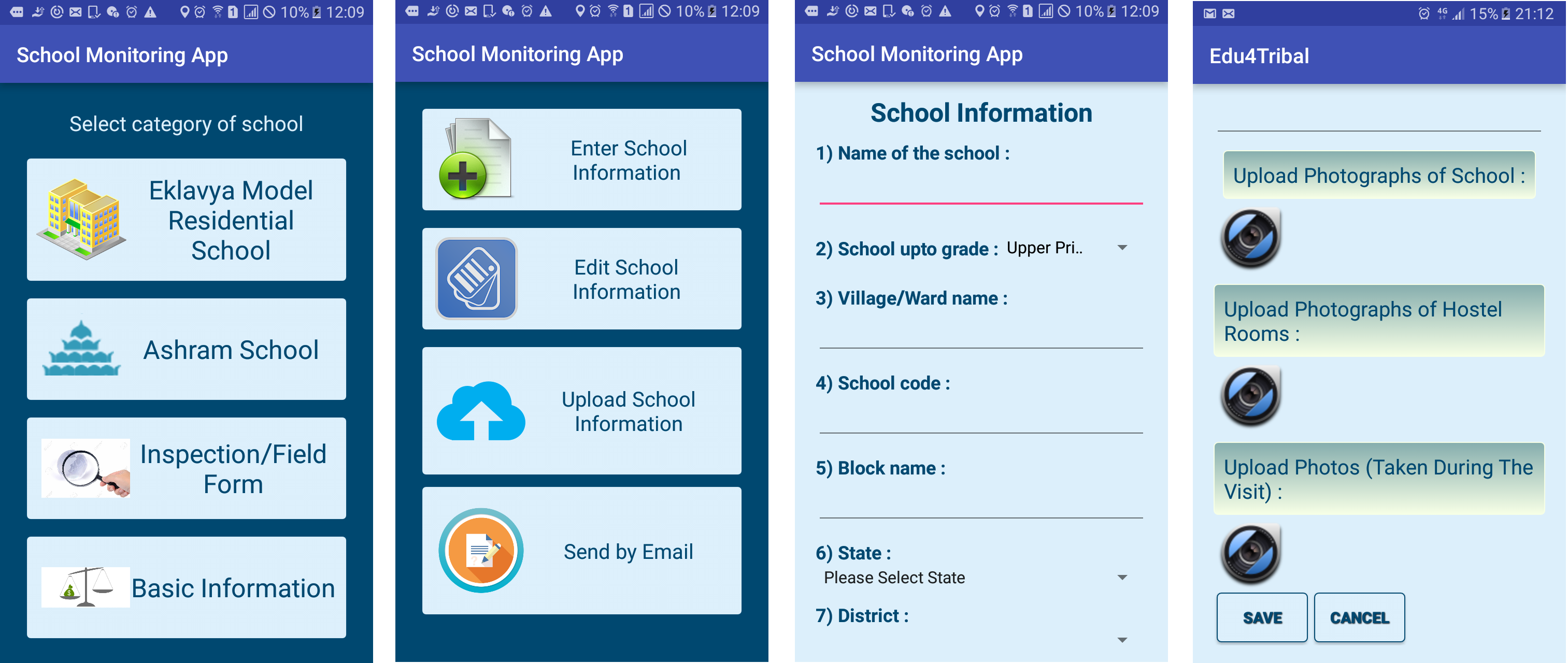
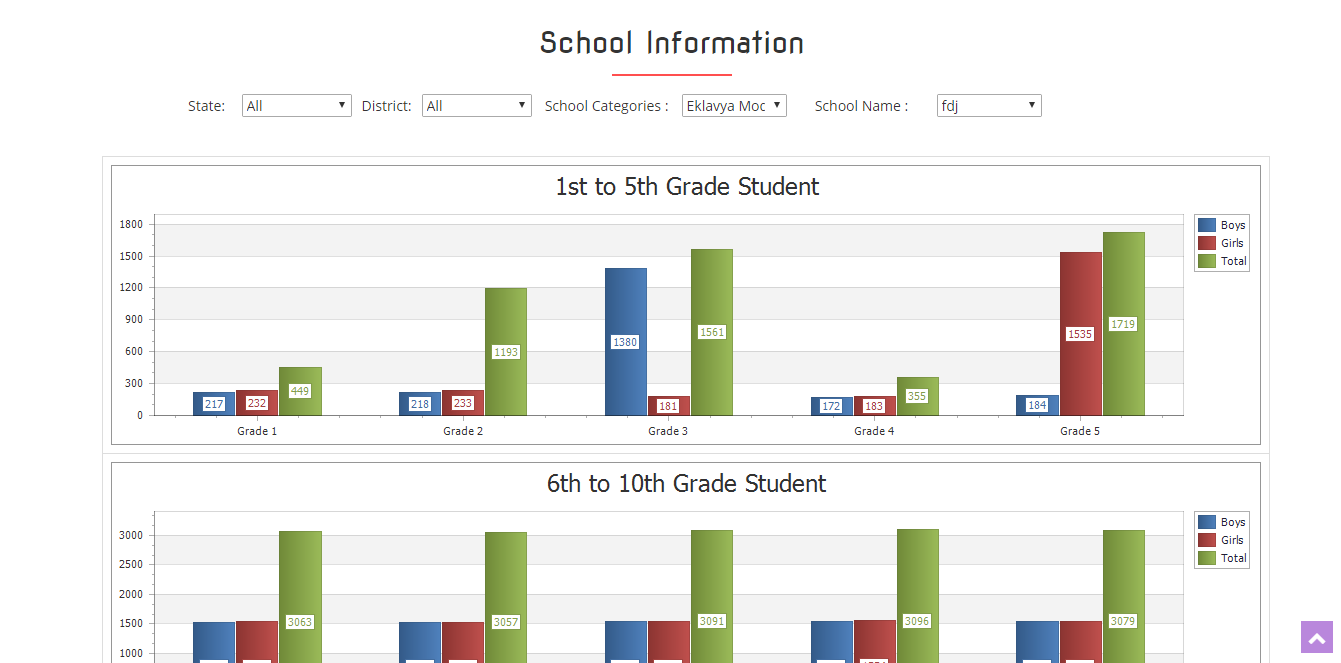
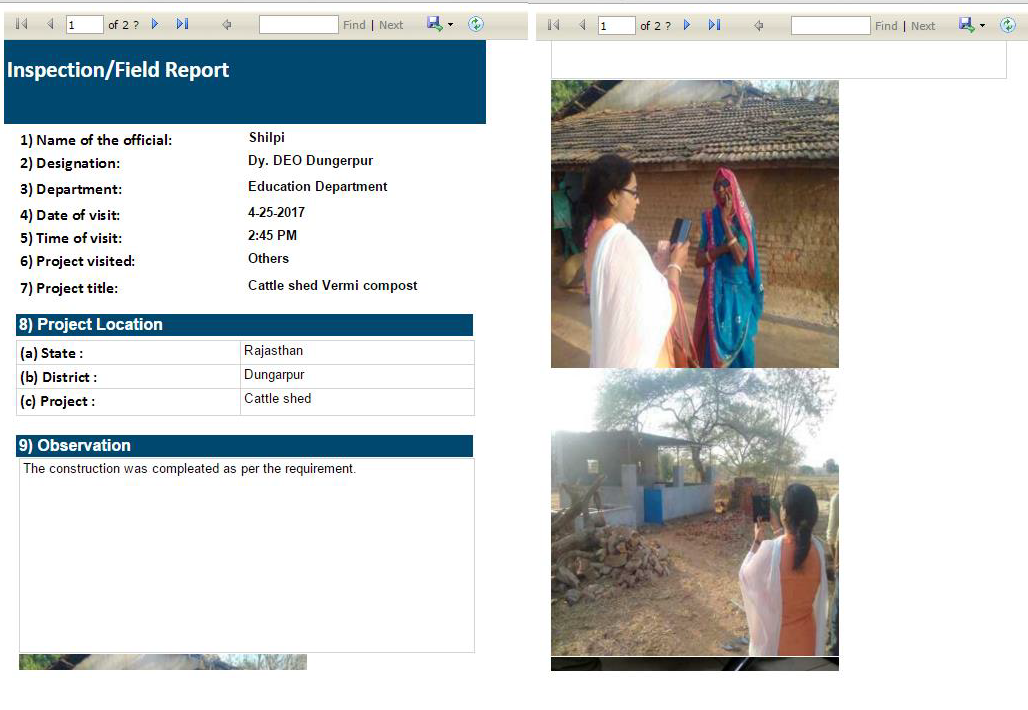
EMRS Project
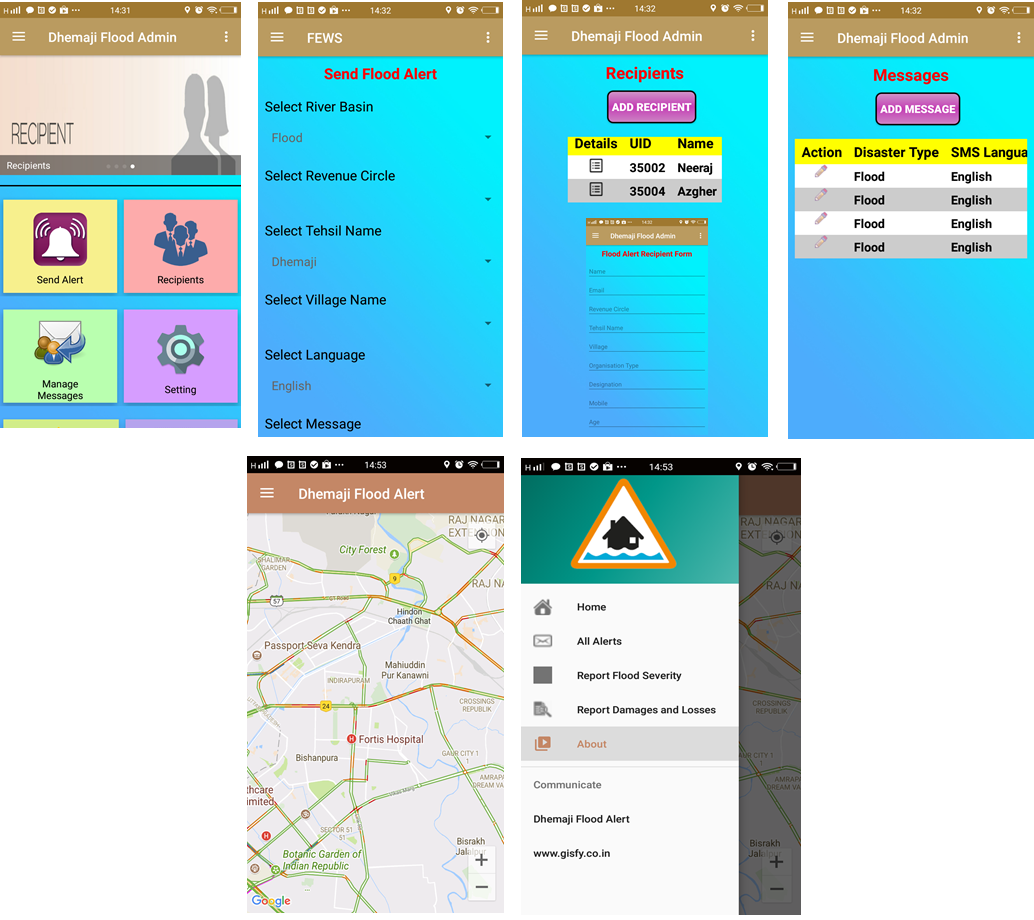
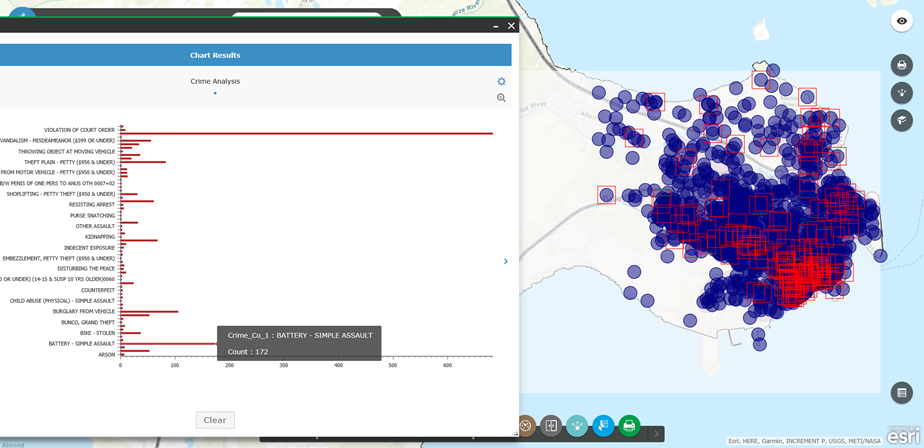
FEWS Project

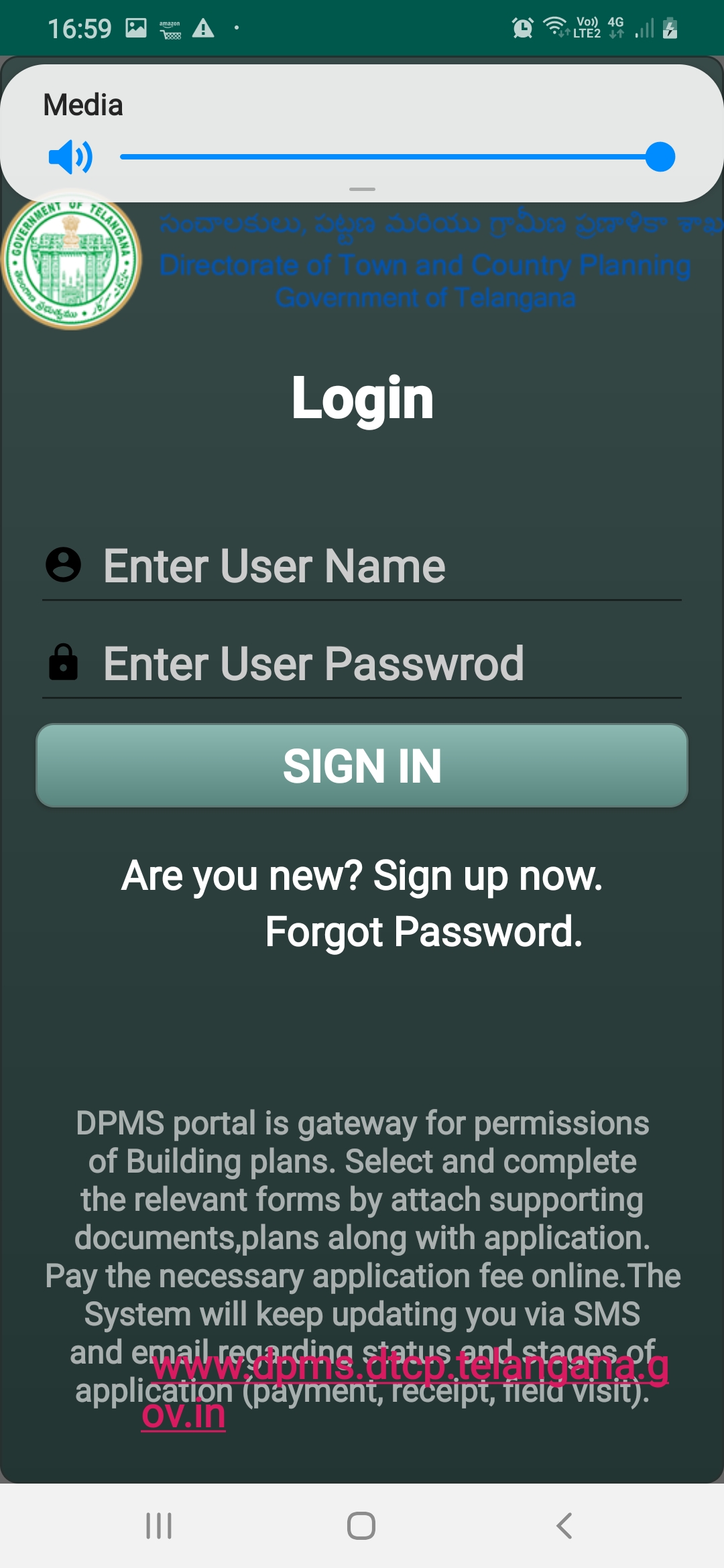
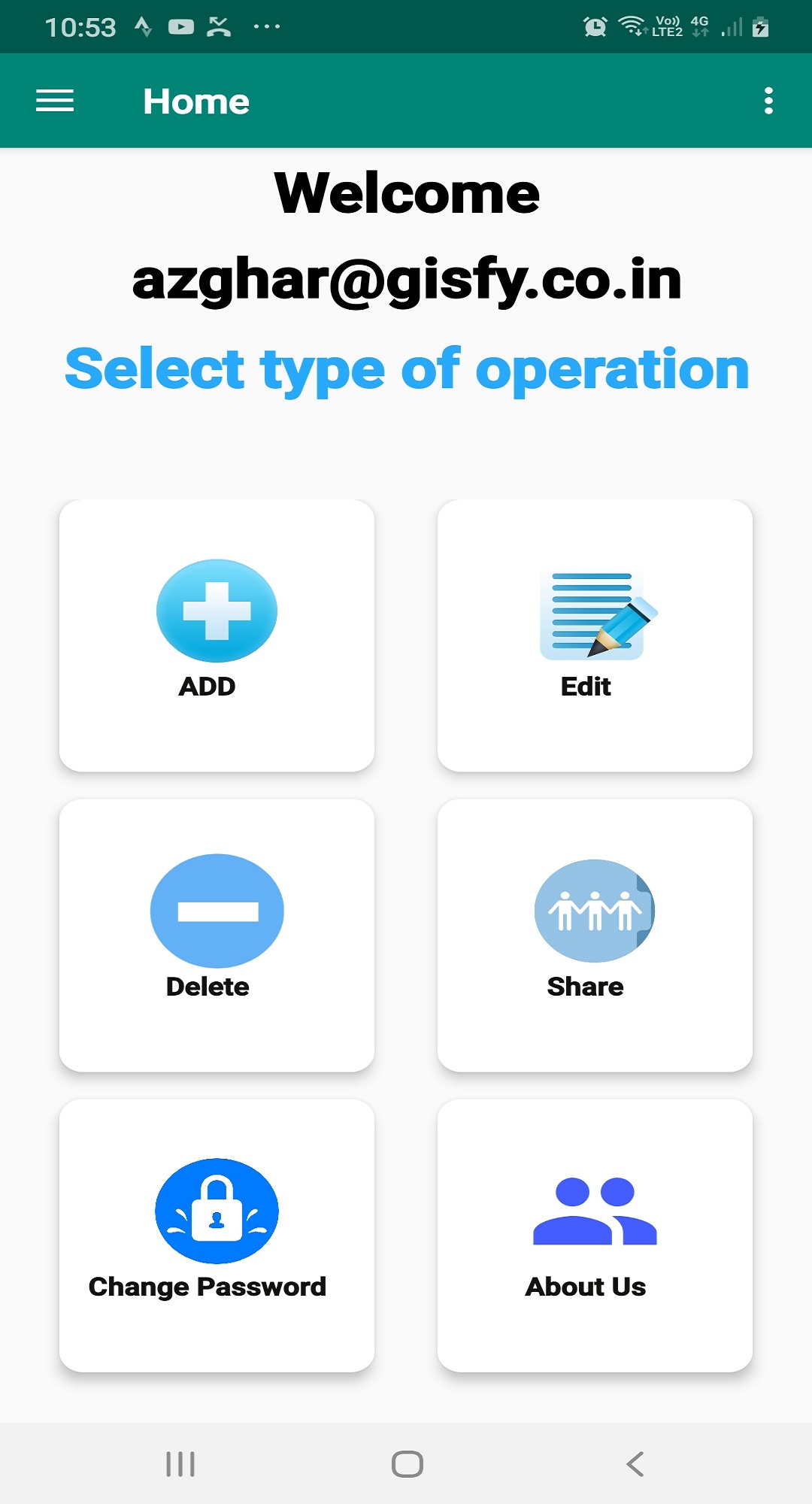
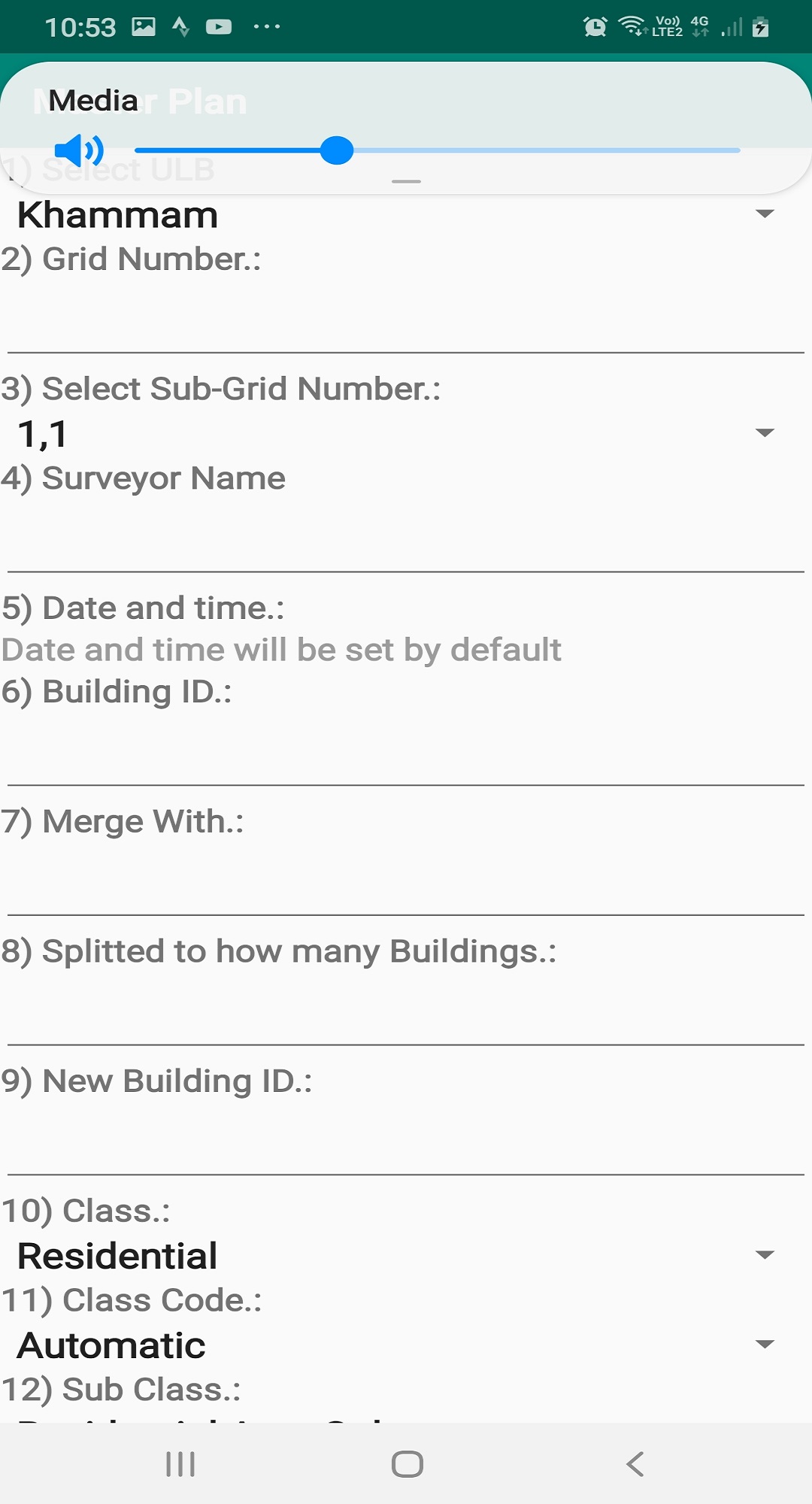
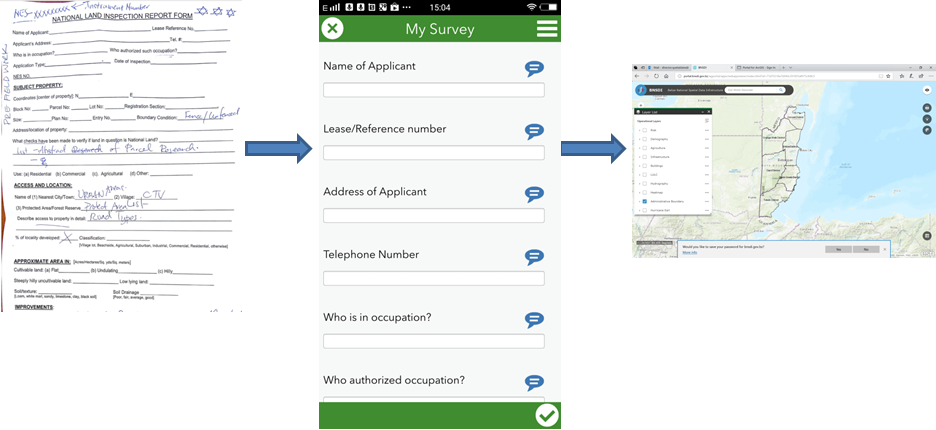
MasterPlan Survey Project

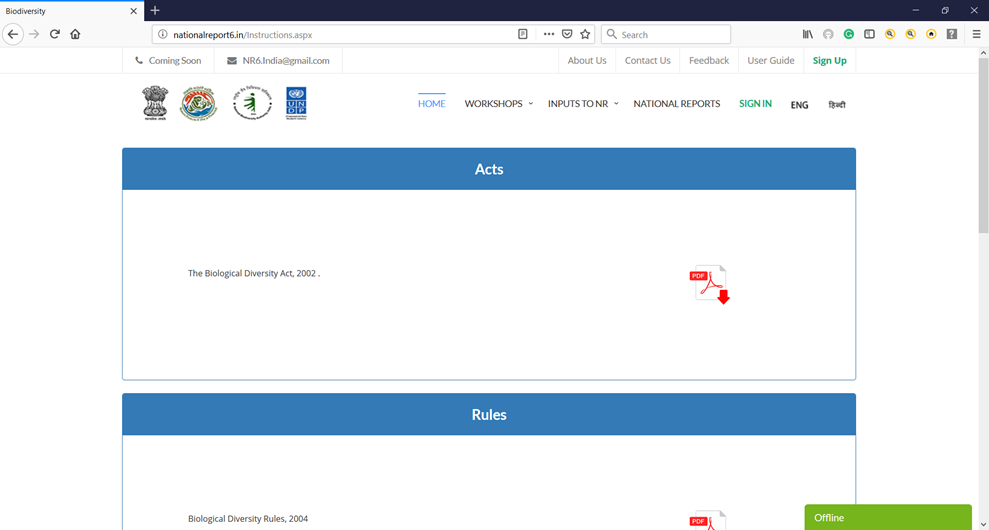
National Biodiversity Report Project
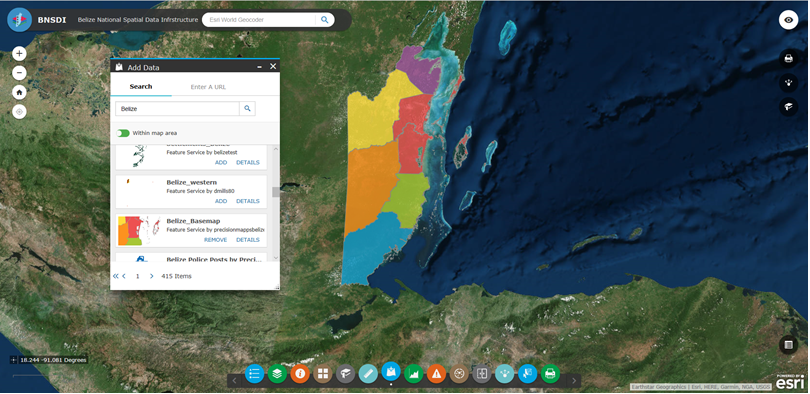
NSDI Project
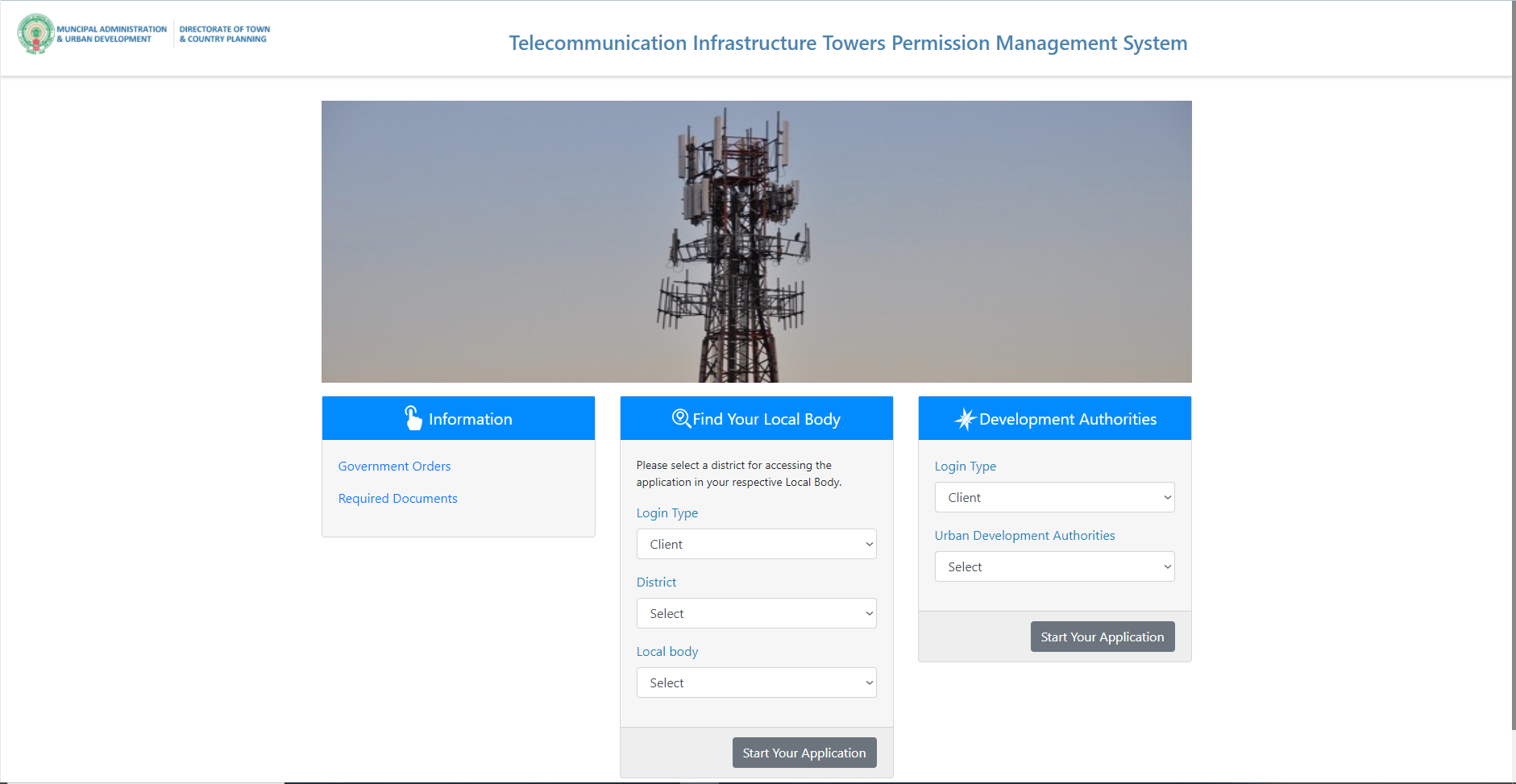
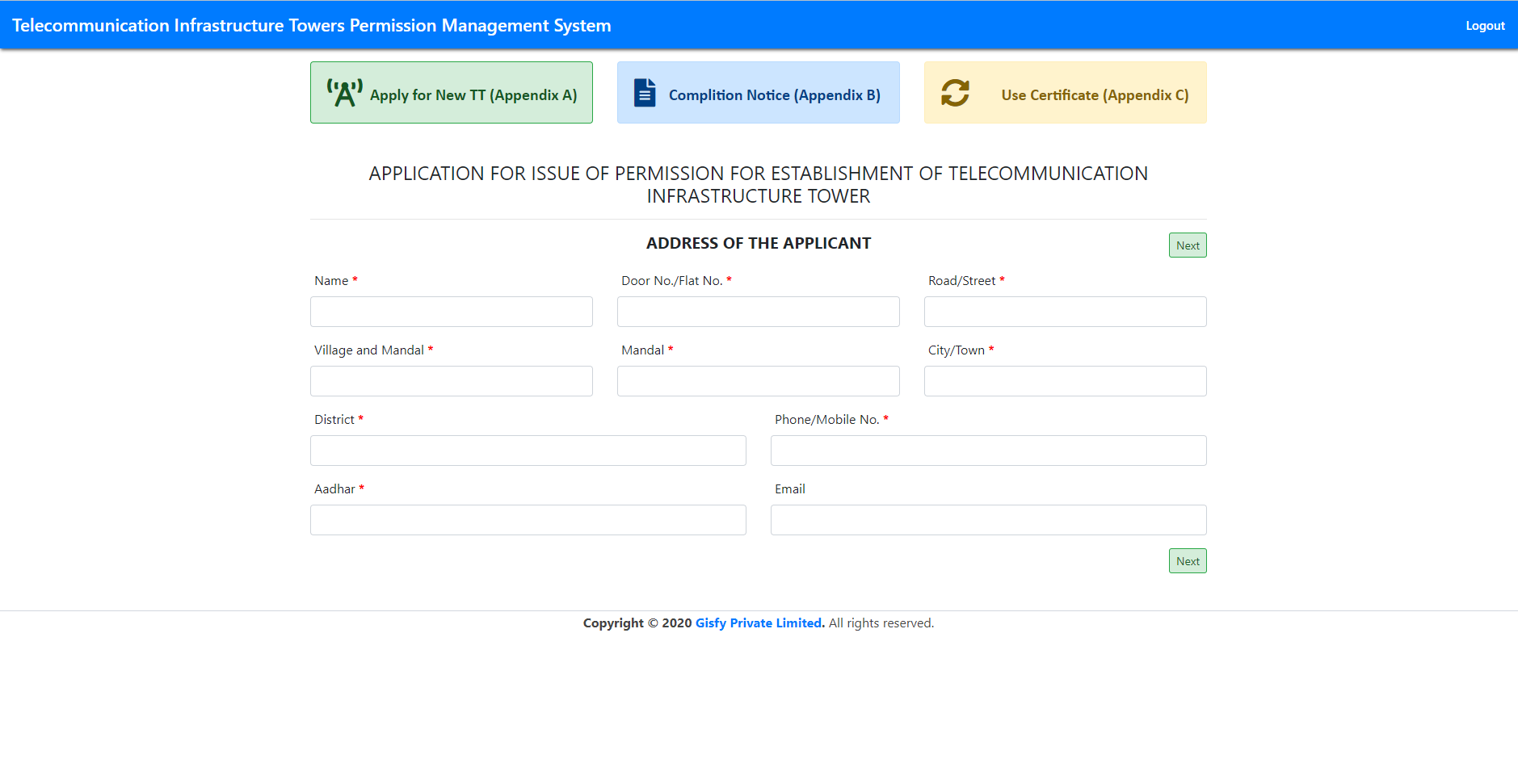
TTPMS Project
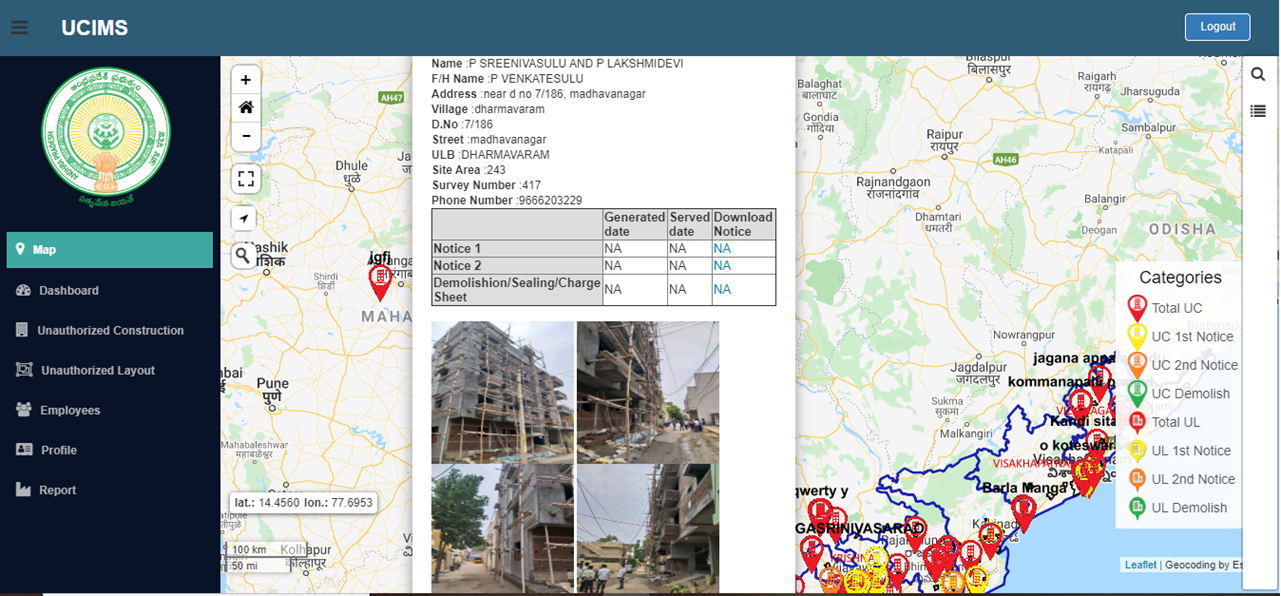
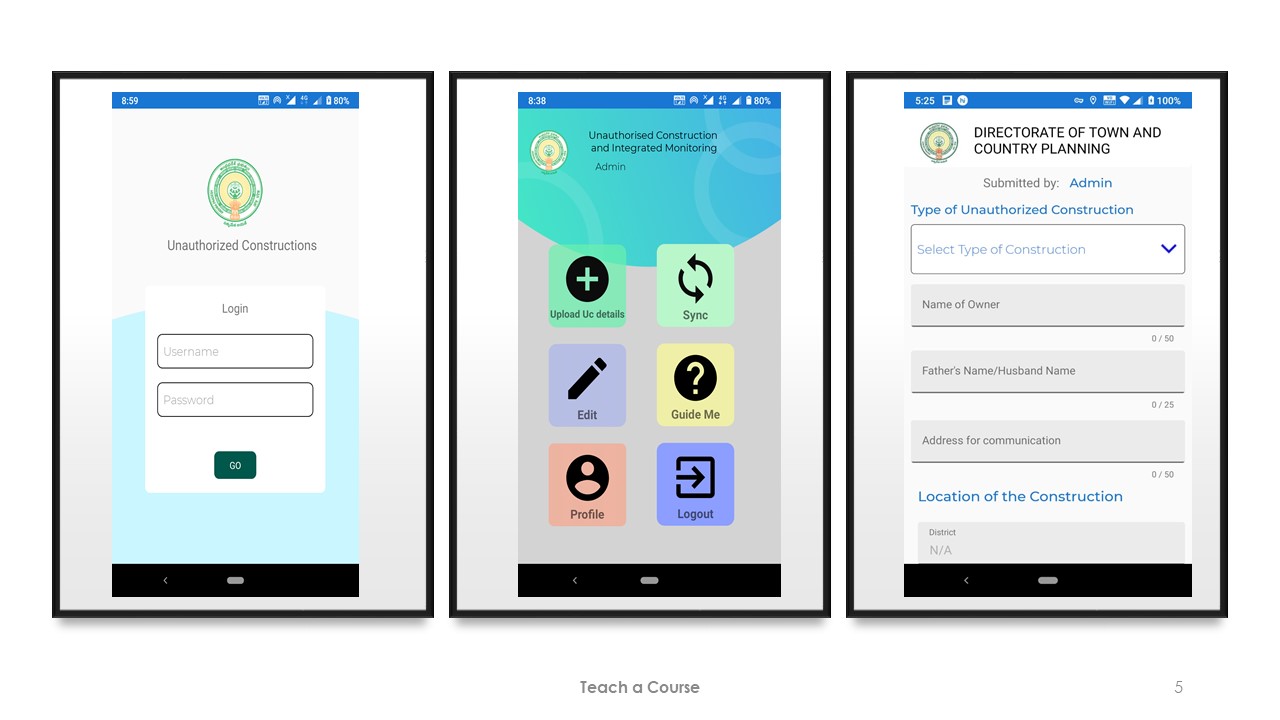
UCIMS Project

Urban asset inventory and maintainance conditions(UAIMC)

Green infrastructure and natural asset

Urban and regional digital twins

Climate change resilience monitoring